Documentation
Modbus RTU/TCP
ModBus is a protocol based on RTU (serial binary) and TCP/IP packets. A connection with IP-Symcon is possible via LAN or serial gateway.

The following devices are supported by IP-Symcon:
Integration in IP-Symcon
First a "ModBus" instance has to be added within IP-Symcon. There are several variants that can be created:
| Instance | Description |
|---|---|
| ModBus Device | Instance, which can map multiple addresses (coils/registers) and supports templates (7.0 and higher) |
| ModBus Coil. | Instance which represents a single address (coil) |
| ModBus Address | Instance which represents a single address (register) |

Many templates can be found in our community: Show templates
The configuration of the parent gateway and I/O instance must then be adapted to the connected device. It must be selected via which protocol and device ID the device is addressed. The device ID is particularly important for RTU connected devices. For devices connected to TCP, this is often device ID 1.
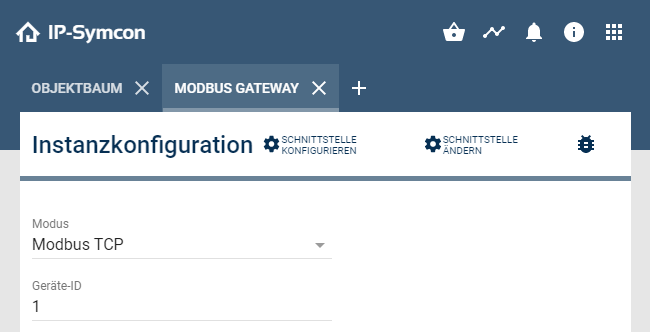
In order to be able to establish a connection to the device, IP address and port (default:502) must be entered in the gateway's parent I/O instance.
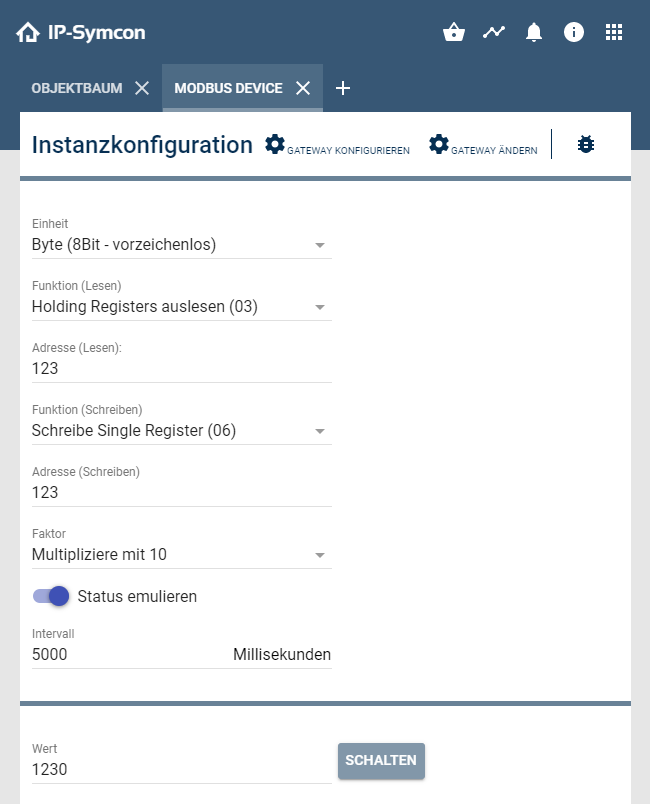
Further configuration (screenshot below) is as follows.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit | Data type of the variable of the device |
| Function (Read) | Function according to which the values are to be read |
| Address (Read) | Device address of the register to be read from |
| Function (Write) | Function according to which the values are to be written |
| Address (Write) | Device address of the register to be written to |
| Factor (Numeric values) | The factor multiplies or divides the received value and writes it to the device variable |
| Length (Strings) | If the length is greater than 0, it defines the precise number of characters (Bytes) queried. Note: 1 register = 2 characters (Bytes) |
| Byte order | Depending on the device, the byte order must be adapted. Often this is not documented, but must be tried out. Big Endian and Little Endian (byte swap) are the common values. |
| Emulate status | "Emulate status" means that the value of the variable is set to the new value if the write command is successful and does not depend on a read command |
| Interval | If the interval is greater than 0, the address (read) is queried cyclically on the ModBus device and the variable of the device is updated |

Due to the fact that we still support 32 bit systems Int64 values are mapped as Float64.
Modbus device
If multiple addresses are to be queried for a device, the Modbus device should be used. Here several addresses can be entered as a table and virtual addresses can be defined.
Configuration:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Addresses | Tabular listing of the defined addresses |
| Configure virtual addresses | Button with which a list of virtual addresses can be defined |
| Byte order | The byte order must be adjusted depending on the device. This is often not documented but has to be tried out. Big Endian and Little Endian (bytes swapped) are the common values. |
| Interval | If the interval is set to greater than 0, the address (read) of the ModBus device is queried cyclically and the device variable is updated. |
| Import template | Using this button, a template of the tables can be quickly inserted. |
| Export template | Through this button, |
| A template can be created from the settings made |
Contents of the address list:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Active | Specifies whether the variable should be created |
| Name | Name, used as variable name |
| Unit | Data type of the register |
| Function (Read) | Function according to which the values should be read |
| Address (Read) | Register to be read from |
| Function (Writing) | Function according to which the values should be written |
| Address (writing) | Register to be written to |
| Profile | Profile, which should get the variable |
Under the expert options, the ident can be customized and a translation for the variable name can also be provided.
Contents of the virtual address list:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Active | The variable is created |
| Name | Name, used as variable name |
| Variable type | Type of variable |
| Profile | Profile of the variable |
| Read | Script that provides the values of the virtual address |
| Write | Script that passes the values to the variables. |
In the read script, all values with their respective idents are available in $VALUES. The new value,
which should load in the variable of the virtual address is simply returned with return. If no value is to be written (e.g. because invalid), null can be returned. (from 7.1)
return ($VALUES["A_3_3_23296"] + $VALUES["A_3_3_23298"] + $VALUES["A_3_3_23300"])/3;
The write script expects an associative array as return, which contains all the idents to be written to. $VALUE contains the new value,
which was requested via RequestAction.
return ["A_3_3_23296" => $VALUE];
FunctionCodes
Depending on the FunctionCode, a suitable address must also be entered. This can be taken from the table.
The table below also provides an overview of which FunctionCode is sent with which parameterization within IP-Symcon:
| FunctionCode | Device address | Read/Write address | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01 (1) | 1 - 10000 | Device address - 1 | Read Coils |
| 0x05 (5) | 1 - 10000 | Device address - 1 | Write Single Coil |
| 0x02 (2) | 10001 - 20000 | Device address - 10001 | Read Discrete Inputs |
| 0x03 (3) | 40001 - 50000 | Device address - 40001 | Read Holding Registers |
| 0x10 (16) | 40001 - 50000 | Device address - 40001 | Write Multiple registers |
| 0x04 (4) | 30001 - 40000 | Device address - 30001 | Read Input Registers |

If, for example, address 40123 is to be written to (FunctionCode = 0x10), the appropriate data type (unit) must be selected and write address 122 (40123 - 40001) entered.

Some manufacturers do not adhere to this convention. It must be checked in the respective instructions or data sheets whether the device address must be subtracted depending on the function code or whether absolute addresses apply
Data types
| Data type | Sign | Bits |
|---|---|---|
| BOOL | unsigned | 1 |
| UINT8MSB | unsigned | 8 |
| UINT8LSB | unsigned | 8 |
| UINT16 | unsigned | 16 |
| UINT32 | unsigned | 32 |
| UINT64 | unsigned | 64 |
| INT8MSB | signed | 8 |
| INT8LSB | signed | 8 |
| INT16 | signed | 16 |
| INT32 | signed | 32 |
| INT64 | signed | 64 |
| FLOAT32 | signed | 32 |
| FLOAT64 | signed | 64 |
| STRING |